Intelligent comprehensive monitoring system for power supply and distribution
1. Overview
With the development of large-scale power supply and distribution stations, the rise of intelligent buildings, and the improvement of industrial automation level, the requirements for power supply and distribution systems are becoming increasingly high, and are developing towards' stronger functionality, higher reliability, and more complete systems'. At the same time, the intelligent comprehensive monitoring system for power supply and distribution has been increasingly applied and popularized, and is constantly advancing towards the direction of "smarter, faster, and more user-friendly".
SY5000 series intelligentPower supply and distribution monitoring systemIntegrated with software computing, device communication, metering protection, status monitoring and other comprehensive automation monitoring functions, it has various advanced functions such as "comprehensive functionality, intelligent operation management, computerized structure, visualized operation monitoring, and user-friendly human-machine interface", fully ensuring the safety and reliability of the operation of the power supply and distribution system. The system collects data information from on-site equipment in the interval layer, completes data reception and conversion through the communication layer, and establishes real-time information exchange with the network layer. Users only need to monitor, analyze, and control the system through the console.
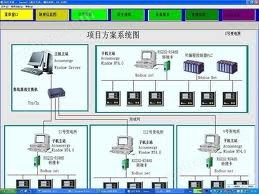
2. System architecture

3. System functions
3.1 Monitoring Function
The system leverages the advantages of various advanced technologies and adopts a layered distributed system structure, dividing the system into network layer, communication management layer, and interval layer to achieve the "four remote" functions on site.
(1) Functions of data acquisition and control system
The collection and processing of routine electrical quantities (including analog quantities, electrical measurements, and switch quantities) for the entire factory.
Circuit breakers, isolating switches, and electrically operated grounding switches for the entire factory;
Main transformer monitoring;
Backup generator monitoring;
DC system;
Communication equipment and power alarm signals;
The status of important feeder switches for factory transformers and DC systems;
The collection of instruments and protection signals in the factory compartment, including protection action information, event sequence recording information, and protection device working status.
(2) Remote signaling range
Circuit breaker, isolation switch, handcart position, and grounding knife position signals.
Action signals for 400V low-voltage instruments and 10kV protection equipment.
System low current grounding signal.
Factory wide alarm signal.
Intelligent DC power panel signal.
Accident signal.
Protect the signal.
The status of the switch.
(3) Telemetry range
The current, voltage, active power, reactive power, active energy, reactive energy, power factor, and frequency of 10kV and 400V incoming lines.
The current, active energy, reactive energy, active power, reactive power, and power factor of a 10kV transformer.
10kV bus voltage.
380V three-phase current, reactive power, and reactive energy.
10kV busbar segmented current.
(4) Remote control range
The entire factory switches on and off.
(5) Remote adjustment range
Remote modification of instrument and relay protection settings.
(6) Terminal power parameter meter
SY72-EGYMulti functional power meter
Product specifications

Wiring terminals
3.2 Report Management
The system runs in real-time to record and recall, and can generate inspection record sheets (daily, monthly, and hourly records, etc.), energy balance sheets, load balance sheets, etc.
3.3 Accurate timing
The system can accept standard timing signals from the Global Positioning System (GPS), has clock synchronization transmission correction measures, supports GPS clock system timing, and ensures that the clock synchronization rate meets the requirements of high accuracy.
3.4 Human Machine Communication
Manually randomly bring up the screen and start printing the report; Locking and commissioning of control; Suppress or restore alarm operations for a telemetry, remote signal, or all; Generate and modify various reports and screens, generate and modify forwarding information tables; Generate and modify databases; Online screen copying; The human-machine operation methods include mouse, keyboard commands, and function keys. The operation menus are all localized in Chinese, and the font and size of Chinese characters are diverse; Print uplink and downlink messages.
4. Human computer interface
4.1 Data Collection

4.2 System Monitoring

4.3 Graphic Display